Export Preflight
Compatibility
This step is only required for documents you need to export to XML.
Export Preflight tags copyedited elements. This means that you need to run all cleanup and copyediting processes before running Export Preflight. See Working with the Typefi Orion ribbon for an overview of the sequential phases.
Run Export Preflight
To run Export Preflight, select Export Preflight from the Advanced Workflows dropdown (Orion → Advanced Workflows → Export Preflight).
Export Preflight checks and tags paragraphs that include the following elements:
Author processing
Export Preflight analyzes paragraphs with author or contributor elements, then correctly tags each element for XML export. When author information is present in a paragraph (for example, author elements prefixed au_), character styles are applied and mapped to other author elements.
This tool identifies which paragraphs contain author information and applies character styles to contributor elements, such as:
- multi-word surnames
- academic degrees
- organisation names
- specific roles
Because author metadata formatting can vary, it's important to carefully review the results of the automatic styling, as manual adjustment of non-standard entries may be necessary.
Character styles
| Element | Character style | Description | Example text |
|---|---|---|---|
| Author | _au | The author's name | Ravinder Mamtani, MD* Sherlock Holmes, Jr. Dr. John Watson, RN, DPM |
| First name Given name | au_fname | The first name(s) or initial(s) of each contributor | RavinderSherlockJohn |
| Surname | au_surname | The surname of each contributor | MamtaniHolmesWatson |
| Generation | au_suffix | The generational suffixes to contributor names | Jr., Junior, or III |
| Degree(s) | au_deg | The academic degrees and other qualifications or appointments that are listed as part of the authorship line. | MDRN, DPM |
| Collaboration | au_collab | The group(s) of contributors | League of Extraordinary Gentlemen |
| Role | au_role | Information about each contributor's role | Associate Professor |
| Prefix | au_prefix | Introductory text before the author line, or prefixes to individual names (such as military ranks or ranks of nobility) | Edited by, Dr. |
Affiliations
Export Preflight targets specific styles based on your configuration. In the default JATS configuration, this is the Affiliations paragraph style. Orion analyzes the entire paragraph where you apply the Affiliations paragraph style. Then, it identifies the structured elements (such as address, city, and state), and automatically applies character styles to each element. If needed, you can manually adjust the character styles to refine the tagging.
Primary language affiliations
To ensure Orion correctly identifies and tags the affiliations, the Affiliations paragraph style must be applied to the associated content.
There are two methods to structure primary language affiliations. In both cases, the placement of the linking superscript character, which links affiliations to authors, is critical for tagging:
- One affiliation per paragraph: Each institution is listed in its own paragraph. The linking character (superscript letter, number, or symbol) must appear at the start of the affiliation paragraph.
- Multiple affiliations in one paragraph: All institutions or organisations are combined in one paragraph. The linking character must immediately precede the specific institution or organisation it links to.
Example

Translated affiliations
Note
Support for translated affiliations may not be available in all configurations.
🔑 Guidelines
- Use the
Affiliations (Translated)style with the correspondingAuthors (Translated)style. This ensures that both author and affiliation translations are correctly parsed. - Maintain the same paragraph formatting methods described in the primary language affiliation section.
- Linking characters can match or differ from the primary language affiliations. Orion identifies links by character style, so you can use different symbols to comply with international style guides while maintaining correct tagging.
Character styles
The table below lists the parts of the affiliation text and the character styles that Orion applies to each element.
| Element | Character style | Description | Example text |
|---|---|---|---|
| Department | C.af_department | The specific department or school within the institution | Camperdown Campus |
| Institution | C.af_institution | The name of the organisation, university, or company (the main body of the affiliation) | University of Sydney |
| Address line | C.af_addr-line | The general line of address (for example, the street number and name) | Quadrangle A14 |
| City | C.af_city | The city component of the institution's address | Sydney |
| State | C.af_state | The state or province of the institution's address | NSW |
| Country | C.af_country | The country component of the address | Australia |
| Postcode | C.af_postcode | The postal code of the institution's address | 2006 |
| Phone | C.af_phone | The phone number | +61 2 9351 2222 |
| Fax | C.af_fax | The fax number | +61 2 9351 7600 |
Exported JATS 1.2 XML examples
The JATS XML example shows the Affiliations (Translated) paragraph style are exported into the <aff-alternatives> element with the distinction made via the language attribute in the <aff> tag.
<aff id="aff1">
<label>1</label>
<institution content-type="dept">School of Chemistry</institution>,
<institution>The University of Sydney</institution>,
<addr-line>
Quadrangle A14,
<city>Sydney</city>,
<state>NSW</state>
<postal-code>2006</postal-code>
</addr-line>
<country>Australia</country>.
</aff> <!-- TRANSLATED LANGUAGE (Spanish) -->
<aff id="aff1-es" xml:lang="es">
<label>1</label>
<institution content-type="dept">Escuela de Química</institution>,
<institution>Universidad de Sidney</institution>,
<addr-line>
Cuadrángulo A14,
<city>Sidney</city>,
<state>NSW</state>
<postal-code>2006</postal-code>
</addr-line>
<country>Аustralia</country>.
</aff>
</aff-alternatives>Keywords
Export Preflight automatically analyzes your paragraphs for keywords then tags XML keyword groups or definition lists based on standard editorial styles. Keywords must be separated by the same character consistently (such as commas or semicolons). Inconsistent separators may prevent individual keywords from being identified correctly.
Keywords are terms used to highlight the subject of the document that improve search results.
The strongest symbols to separate keywords are:
- semicolons
; - em dashes
— - bullets (•)
Keywords separators, listed in priority
;,tabdash
These characters aren't typically used within the text of a single keyword. When a semicolon, em dash, or bullet is found in a paragraph containing keywords, Export Preflight will use that character to separate the paragraph into individual keywords.
If no semicolons, em dashes, or bullets are found in the paragraph containing keywords, Export Preflight will check for additional characters:
- tabs
- em spaces
- commas (followed by a space) (
,) - slashes with spaces on either side (
/)
Character styles
| Element | Character style | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword title | kwd_title <title> </title> | The keyword title |
| Keyword | kwd_kwd <kwd> </kwd> | The keywords in the paragraphs |
Example
Keywords: Chickpea; Physiological trait, Genotypes, QTLs, Head stress, Climate resilience, Staphylococcus aureus.
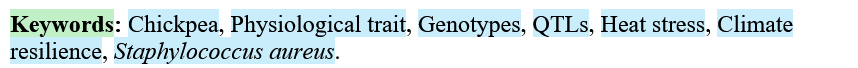
This paragraph will be correctly processed during XML export.
Exported JATS 1.2 XML:
<kwd-group>
<title><bold>Keywords:</bold> </title>
<kwd>Chickpea</kwd>
<kwd>Physiological trait</kwd>
<kwd>Genotypes</kwd>
<kwd>QTLs</kwd>
<kwd>Head stress</kwd>
<kwd>Climate resilience</kwd>
<kwd><i>Staphylococcus aureus<i></kwd>
</kwd-group>Abbreviations
Export Preflight automatically analyzes your paragraphs for abbreviations then tags keyword groups or definition lists based on standard editorial styles.
Abbreviations appear as term-definition pairs. In the default JATS configuration, this is the Abbreviations paragraph style. Orion analyzes paragraphs where you apply the Abbreviations paragraph style; then, it identifies the terms and definitions, and automatically applies character styles to each element.
Note
Abbreviations must be separated by the same character, consistently (such as a commas or semicolons). Inconsistent separators may prevent individual abbreviations from being identified correctly.
Primary language abbreviations
The Abbreviations paragraph style may be used for one or more paragraphs containing a list of abbreviations.
Separate term-definition pairs with one of the following:
tab- semicolon
; - em dash
—
Separate individual terms and definitions with one of the following:
- en dash
– - comma (followed by a space) (
,)
Translated abbreviations
Note
Support for translated abbreviations may not be available in all configurations.
🔑 Guidelines
- Use the
Abbreviations(Translated)paragraph style in the same way as the primary language abbreviation style (including, the use of the specific separators). In the XML output, primary and translated language abbreviations are listed together in the<def-list>element.
Character styles
| Element | Character style | Description | Example text |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation title | C.abbrev_title <title> </title> | The title of the abbreviation | Abbreviations |
| Term | C.abbrev_term <term> </term> | The abbreviation term | JATS |
| Definition | C.abbrev_def <def> </def> | Full form or explanation of the abbreviation | Journal Article Tag Suite |
Example

Publication history
Export Preflight will automatically identify, categorise, and tag different types of dates within your document.
Orion will identify a date type by the consistent keywords you use then apply the correct tag to that date. For example, if it identifies the date "Accepted: 17 July 2024" it will tag the date with an accepted attribute.
Keywords to use to introduce dates:
- Received
- Updated
- Revised
- Accepted
- Submitted
- Dates related to online posting or publication (for example, "Online First," "Published").
Character styles
| Element | Character style | Description | Example text |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date format | C.date_type @date-type=" " | The descriptive text indicating the publication stage. This style triggers the export process to generate the corresponding @date-type attribute in the XML, for example @date-type="received". | Date received, Accepted |
| Day | C.date_day <day> ,</day> | The numerical day of the month | Numerical value: 1 through 31 |
| Month | C.date_month <month> </month> | The month name, standard abbreviation, or numerical value. | Format: Word: DecemberAbbreviation: Dec Numerical value: 12 |
| Season | C.date_season <season> </season> | The season name. | Example: Spring |
| Year | C.date_year <year> </year> | Identifies the four-digit year. | Format: YYYY |
Date formatting best practices
To ensure accurate data recognition and avoid ambiguity:
- Use four-digit years
- If you use numerical dates, use the ISO 8601 format (
YYYY-MM-DD), for example2024-07-17is read as July 17, 2024. - Use full month or season names, or standard three-letter abbreviations
Example

Date separators
Use the following characters to separate date elements (day, month, year):
- Slashes (
/) - Colons (
:) - Hyphens (
-) - Periods (
.)
Exported JATS 1.2 XML:
<history>
<date date-type="received">
<day>10</day>
<month>04</month>
<year>2024</year>
</date>
<date date-type="rev-recd">
<day>10</day>
<month>07</month>
<year>2024</year>
</date>
<date date-type="accepted">
<day>17</day>
<month>07</month>
<year>2024</year>
</date>
</history>Run-in headings
Run-in headings are concise labels that appear on the same line as the start of the text they introduce (often used in abstracts, glossaries, or lists).
Export Preflight uses the Labelled Paragraphs style set to identify which paragraph styles should have run-in headings tagged. To ensure run-in headings are automaticlly tagged with the appropriate character style, check the following:
- The run-in heading is in bold and located at the beginning of the paragraph
- The paragraph style must be listed in the
Labelled Paragraphsstyle set in Typefi Orion Compass - The appropriate paragraph style must be applied to the paragraph containing the run-in heading (for example,
Right Running HeadorLeft Running Head).
Example
Main heading: Start of text that main heading introduces.